Kubernetes是一個可以幫助我們管理微服務的系統,為了因應功能項的不同,Kubernetes中也衍生出了各式各樣的objects,並透過yaml來部署與管理這些objects。
因為在Cluster當中,有著許多不同功能項的objects再加上不同的環境需要不同的變數與設定檔,導致我們需要維護相當多的yaml。
此外,有些功能性常見的服務,像是database存在於Cluster當中,也會需要相當多的yaml,這時我們也會希望有個registry能夠直接去pull這些yaml下來直接使用。
基於種種理由,我們現在要來介紹Helm為何何物!
Helm簡單來說就是個管理諸多kubernetes設定檔的工具,他會把一個Kubernetes 服務中許許多多的yaml檔都打包成一個名為chart的集合。再透過給定參數的方式去管理這些所有的yaml檔。
這樣說好像有點抽象,下面我們會來解說helm的workflow,並講解每個parts所做的事情。
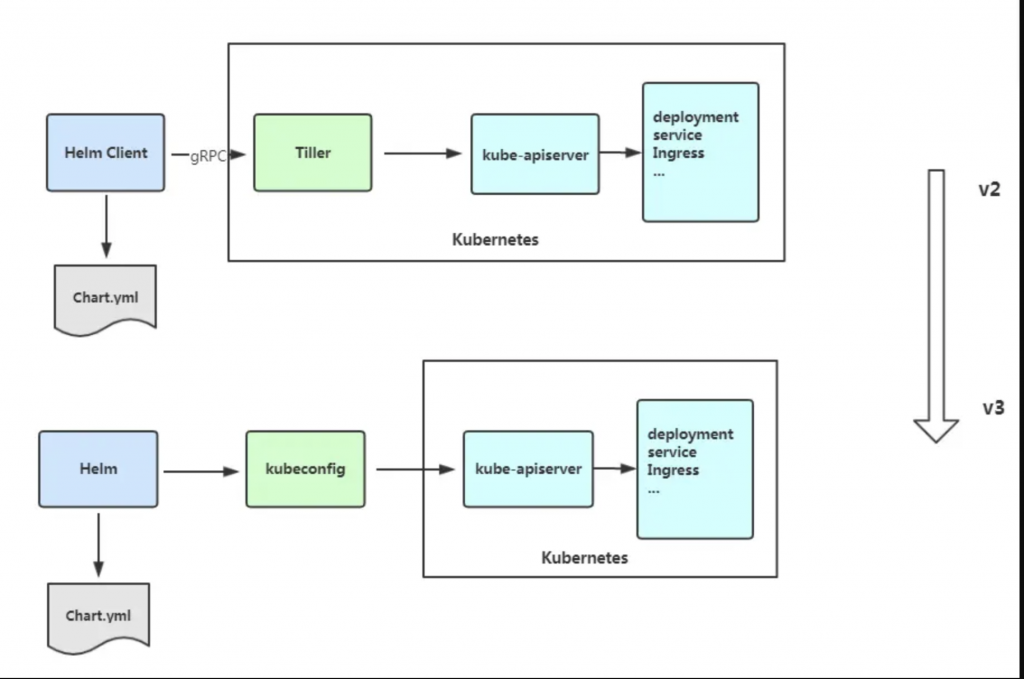
首先,Helm正處於V2到V3的過渡期,因此本篇文會以Helm3為主來解說。
由2到3最大的差異就在於Helm3不在需要透過Tiller去與Kubernetes進行溝通,現在Helm會直接透過kubeconfig用類似於kubectl的方法去直接的與kube-apiserver進行訪問,因此以後不需要再用helm init來初始helm,也不用在遇到因為Tiller所產生的坑了。
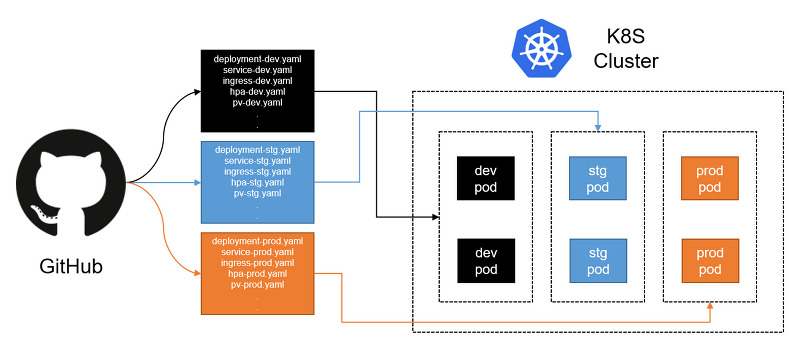
原先,我們可能會透過不同branch的切換,來部署特定服務在不同的environments上。
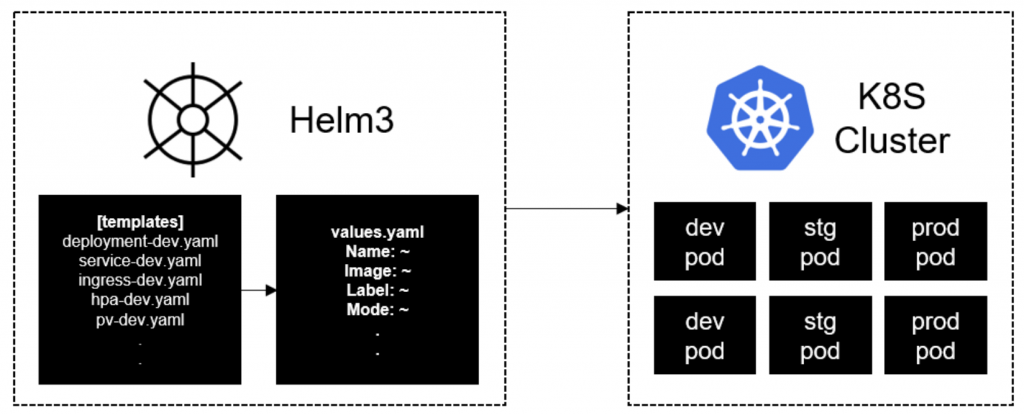
現在,我們則是透過Chart來維護同一份yaml檔,並透過Helm來進行部署,這也大大降低了維護不同環境所帶來的複雜性。
Through brew
$ brew install kubernetes-helm
Through choco
$ choco install kubernetes-helm
$ curl https://baltocdn.com/helm/signing.asc | sudo apt-key add -
$ sudo apt-get install apt-transport-https --yes
$ echo "deb https://baltocdn.com/helm/stable/debian/ all main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/helm-stable-debian.list
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install helm
$ helm version
version.BuildInfo{Version:"v3.3.4", GitCommit:"a61ce5633af99708171414353ed49547cf05013d", GitTreeState:"dirty", GoVersion:"go1.15.2"}
helm repo add
$ helm repo add official https://kubernetes-charts.storage.googleapis.com
"official" has been added to your repositories
$ helm repo list
NAME URL
official https://kubernetes-charts.storage.googleapis.com
helm search repo
這邊我們以jenkins為例
$ helm search repo jenkins
NAME CHART VERSION APP VERSION DESCRIPTION
official/jenkins 2.5.4 lts DEPRECATED - Open source continuous integration...
helm show values /
$ helm show values official/jenkins
# Default values for jenkins.
# This is a YAML-formatted file.
# Declare name/value pairs to be passed into your templates.
# name: value
## Overrides for generated resource names
# See templates/_helpers.tpl
# nameOverride:
# fullnameOverride:
# namespaceOverride:
# For FQDN resolving of the master service. Change this value to match your existing configuration.
# ref: https://github.com/kubernetes/dns/blob/master/docs/specification.md
...etc
helm install /<chart_path>
$ helm install jenkins official/jenkins
WARNING: This chart is deprecated
NAME: jenkins
LAST DEPLOYED: Thu Oct 15 10:37:09 2020
NAMESPACE: default
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
NOTES:
*******************
****DEPRECATED*****
*******************
* The Jenkins chart is deprecated. Future development has been moved to https://github.com/jenkinsci/helm-charts
1. Get your 'admin' user password by running:
printf $(kubectl get secret --namespace default jenkins -o jsonpath="{.data.jenkins-admin-password}" | base64 --decode);echo
2. Get the Jenkins URL to visit by running these commands in the same shell:
export POD_NAME=$(kubectl get pods --namespace default -l "app.kubernetes.io/component=jenkins-master" -l "app.kubernetes.io/instance=jenkins" -o jsonpath="{.items[0].metadata.name}")
echo http://127.0.0.1:8080
kubectl --namespace default port-forward $POD_NAME 8080:8080
3. Login with the password from step 1 and the username: admin
4. Use Jenkins Configuration as Code by specifying configScripts in your values.yaml file, see documentation: http:///configuration-as-code and examples: https://github.com/jenkinsci/configuration-as-code-plugin/tree/master/demos
For more information on running Jenkins on Kubernetes, visit:
https://cloud.google.com/solutions/jenkins-on-container-engine
For more information about Jenkins Configuration as Code, visit:
https://jenkins.io/projects/jcasc/
helm list
$ helm list
NAME NAMESPACE REVISION UPDATED STATUS CHART APP VERSION
jenkins default 1 2020-10-15 10:37:09.212025 +0800 CST deployed jenkins-2.5.4 lts
$ kubectl get pod --watch
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
jenkins-75867f68c8-nv45m 1/2 Running 0 117s
jenkins-75867f68c8-nv45m 2/2 Running 0 2m20s
$ helm fetch official/jenkins
$ ls -l
total 240
-rw-r--r-- 1 flynnsun staff 473 10 5 17:48 Dockerfile
-rw-r--r-- 1 flynnsun staff 14 10 5 17:48 README.md
drwxr-xr-x 4 flynnsun staff 128 10 5 17:48 app
-rw-r--r-- 1 flynnsun staff 795 10 5 17:48 base.yaml
-rw-r--r-- 1 flynnsun staff 3397 10 6 13:08 convert.py
-rwxr-xr-x 1 flynnsun staff 287 10 5 17:48 create_image.sh
-rwxr-xr-x 1 flynnsun staff 63 10 5 17:48 docker-entrypoint.sh
-rw-r--r-- 1 flynnsun staff 53303 10 15 10:52 jenkins-2.5.4.tgz
$ tar -xvf jenkins-2.5.4.tgz
這樣我們就能下載了Jenkins chart的code,之後也能夠透過更改values去匹配我們GCP的其他物件。
helm uninstall
$ helm uninstall jenkins
release "jenkins" uninstalled
$ helm create ironman
Creating ironman
這時我們就建立了一個名為ironman的sample chart
$ cd ironman
$ tree
.
├── Chart.yaml
├── charts
├── templates
│ ├── NOTES.txt
│ ├── _helpers.tpl
│ ├── deployment.yaml
│ ├── hpa.yaml
│ ├── ingress.yaml
│ ├── service.yaml
│ ├── serviceaccount.yaml
│ └── tests
│ └── test-connection.yaml
└── values.yaml
3 directories, 10 files
從上面檔案結構可以看到,我們透過編輯values.yaml,就可以對所有的yaml檔做到版控與管理,並透過install/delete的方式做到一鍵部署/刪除。
雖然鐵人賽到了尾聲(第三十篇),但Kubernetes世界很大,所以我們的旅程依然會繼續(但可能不會維持日更了),Helm的部分由於篇幅關係,我們會在下章節繼續解說如何將目前Kubernetes components yaml轉換成使用helm的chart來維護與部署,有興趣的讀者能夠期待day-31。

雖然鐵人賽即將落幕,但我們的Kubernetes獸依然會持續的強化並加強配備,期許我們能夠在devOps能夠習得更多的技能!
https://helm.sh/docs/intro/install/
